Excessive Obesity Treatment by Laparoscopic Surgery

Obesity treatment by laparoscopic surgery usually is recommended to the people who are excessively obese. In laparoscopic surgery, a special telescope (laparoscope) is used, whereby the stomach can be seen through a small incision in the abdomen.
In this article, the followings are going to be explained:
- What does the excessive obesity mean?
- excessive Obesity treatment with surgical and pharmaceutical procedures
- How is laparoscopy surgery done?
- What happens after laparoscopic surgery?
- The expected results of this surgery
What does the excessive obesity mean?
Excessive obesity means that a person’s weight is at least 100 pounds or 45.5 pounds more than the ideal weight (this definition is based on the height and weight tables of Metropolitan Life Insurance Company). About 3-5% of adults in the United States are obese. This problem is associated with dangerous diseases such as high blood pressure, diabetes, vascular disease, etc.
BMI is one of the most accurate criteria for obesity evaluation. In fact, BMI is an index for showing the body mass and is evaluated as follow:
BMI less than 18.5 = underweight
BMI Between 18.5 and 24.9 = normal
BMI between 25 and 29.9 = overweight
BMI equal 30 and over = obese
There are several methods for Obesity Treatment including low calorie diets, medications, behavioral changes, and exercise therapy.
However, the only effective treatment of excessive obesity is surgical method which is completely proven.
The causes of excessive obesity
The reasons for obesity are difficult to detect. Probably many factors contribute to this problem. In an obese person, the point of energy storage adjustment is very high. The changes occurred in this adjustment point may be due to excessive calorie intake, low metabolism with low energy consumption, or both. In addition, studies have declared that the excessive obesity may be inherited.
The cause of excessive obesity is likely to be a combination of genetic, psychological, environmental, social, and cultural effects that are mutually associated with complex disorders in appetite regulation and energy metabolism. It seems that the excessive obesity is not just caused by the patient’s lack of personal control and usually other factors are involved.
Obesity treatment methods
Medications
The National Institutes of Health announced in 1991 that except in very rare cases, no long-term non-surgical method is effective for the treatment of excessive obesity. Moreover, observations have shown that all excessively obese people who have been treated with non-surgical methods have recovered their lost weight within 5 years.
Although many prescribed and over-the-counter medications are used to treat the excessive obesity, it does not seem that any of them has a long-lasting effect, because the loss of weight is returned when discontinuing these medications. In some cases, behavioral changes (low calorie diet and physical activity) also can decrease a little bit of overweight. Through these procedures, half a kilo to one kilo can be decreased within a week but it is possible that all the lost weights return after 5 years.
Surgical treatments
Over the past 40-50 years, several surgeries have been designed for weight loss. The operations that most surgeons are familiar with include:
- Vertical banded gastroplasty
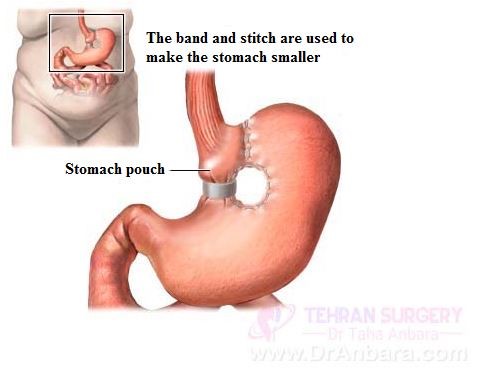
This procedure consists of creating a small pouch restricting the food inlet to the lower stomach. The inlet duct is reinforced by a band preventing disorder and distortion.
- Gastric banding (adjustable and non-adjustable)
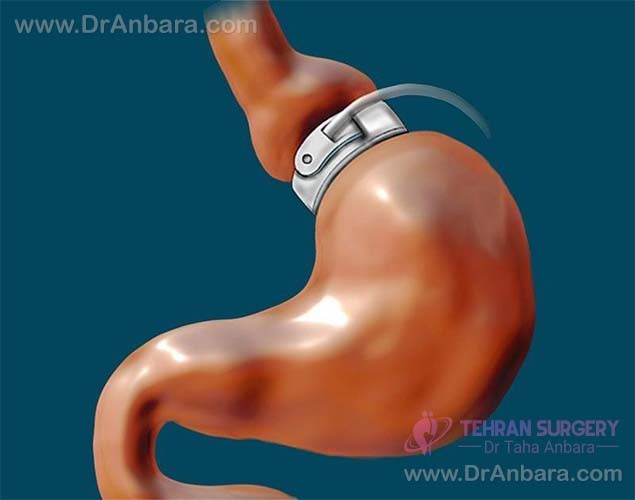
Gastric banding involves fastening a half-inch belt (approximately 1.3 cm) around the upper part of the stomach creating a small pouch and a fixed inlet to the lower stomach. If the banding is adjustable, it will be filled with sterile saline. When the solution is added, the inlet becomes narrower causing the food move harder from the small pouch.
- Roux–En–YGastric Bypass
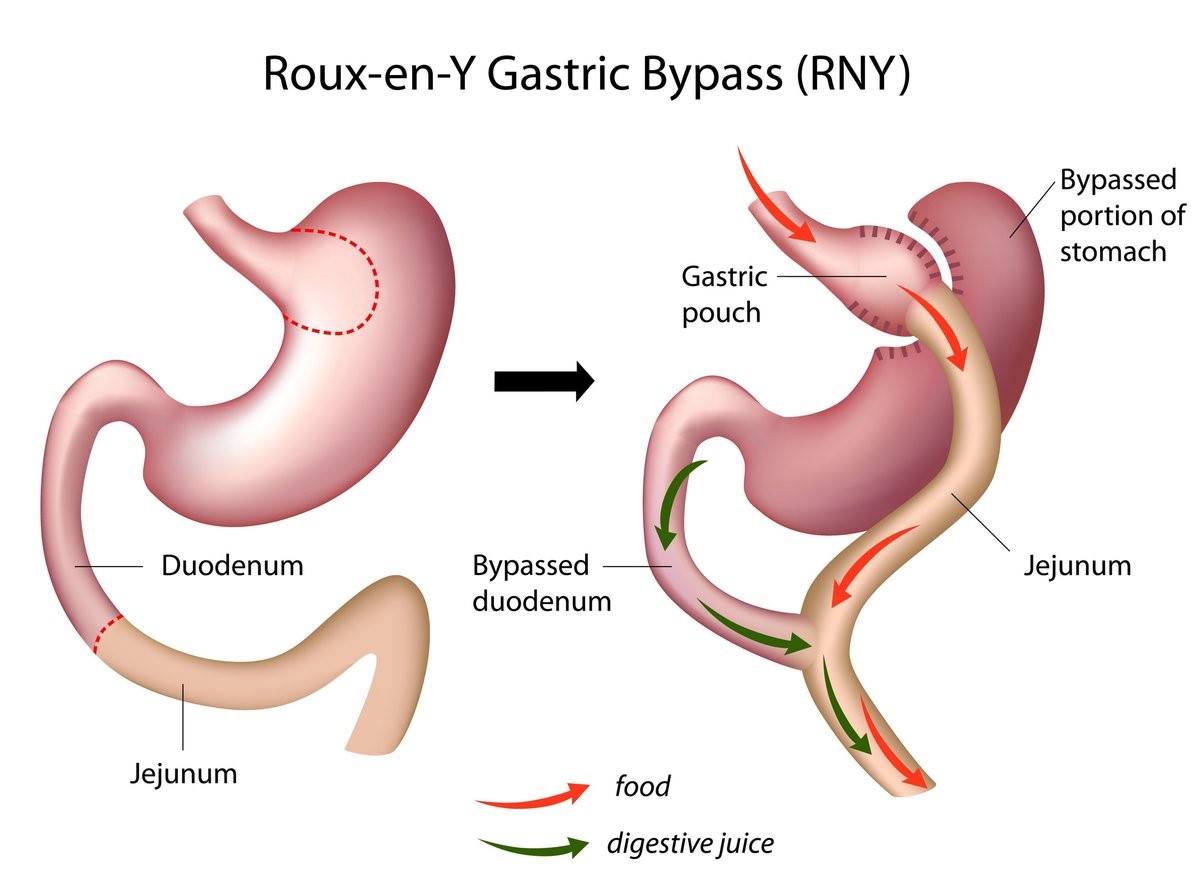
In gastric bypass, the stomach is divided and a small pouch is created from the stomach tissue. The new small pouch is connected to the beginning of small intestine forming a Y-shaped limb.
- Sleeve gastrectomy
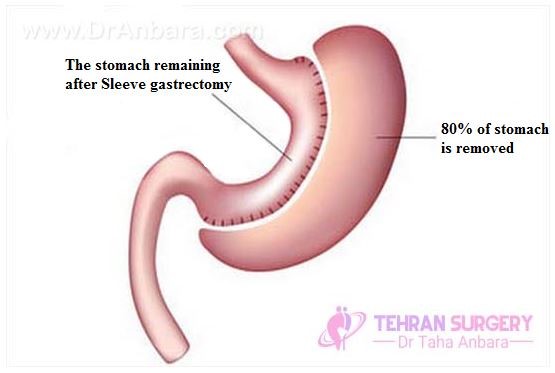
In sleeve gastrectomy, surgeon removes a part of stomach. The remainder will then look like a tube. The new stomach cannot keep much food inside. In addition, this leads the hormone associated with appetite to be produced less and thus, you eat less. Sleeve gastrectomy does not affect the absorption of calories and nutrients in the intestine.
- Sleeve gastrectomy with duodenal switch
This surgery like sleeve gastrectomy is associated with removal of stomach’s major portion. The gate conducting the food toward the small intestine is removed along with the initial part of the small intestine.
Then, the surgeon blockades the middle part of the intestine and directly connects the terminal part to the initial segment of the small intestine. This action is called duodenal switch.
The separated part of intestine is not removed from the body. Rather, it is connected to the end of intestine. This causes the bile and pancreas sap to flow through this part of intestine. This is referred to as bile and pancreas deviation. This surgery aims to make the food to bypass the major portion of small intestine and consequently, less calories and nutrients are absorbed. In this type of surgery, the stomach gets smaller, also fewer calories is absorbed.
What are the advantages of laparoscopic surgery?
- Reduced postoperative pain
- Less hospitalization
- Less scars
- Quick return to everyday activities
- Aesthetic improvement
How is laparoscopy done?
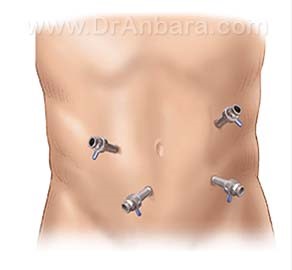
In laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon creates small incisions of 1.2 to 1.4 inches (approximately 3 to 3.5 cm) on the abdomen to allow the insertion of trocars (narrow tubes) into the abdomen and hereby access to the abdomen. A laparoscope attached to a small camera enters into the body through a small trocar. This small camera films the stomach and other abdominal organs showing it on screen so that the surgeon can observe internal state of the body clearly. Usually 4-6 incisions are created and the trocars are located on the incisions in a way that the surgeon using them can carry out the surgery by special instruments.
What happens in the surgery day?
- You go to the hospital on the morning of surgery.
- Before surgery, you should wear a hospital suit and prepare for surgery.
- A member of the medical staff injects you an anesthetic drug to keep calm during surgery.
- Most preoperative medications are essential.
- You visit an anesthetist and talk about the effect of anesthetic drug
- You undergo general anesthetic surgery, i.e. you are completely asleep during the surgery. The effect of this type of anesthetic usually lasts for some hours.
- After surgery, you are taken to the recovery room to fully revive. When you come around, you are taken to your room.
- Most patients are hospitalized about 24 hr, but some may need more to complete their recovery.
Expected results after laparoscopic surgery
Weight loss
Most people who had undergone the laparoscopic surgery have reported that they have lost at least 50% of their weight after one year. The weight loss process lasts about 18-24 months for all kinds of bariatric surgery. Your weight may increase slightly after 2-5 years which is completely normal.
The impact of surgery on obesity-related diseases
After the bariatric surgery and weight loss, the diseases associated with obesity like sleep apnea, diabetes, high cholesterol and blood pressure will be improved. Some patients had reported that their mental status and mood also have improved after surgery.