Obesity and fatty liver disease
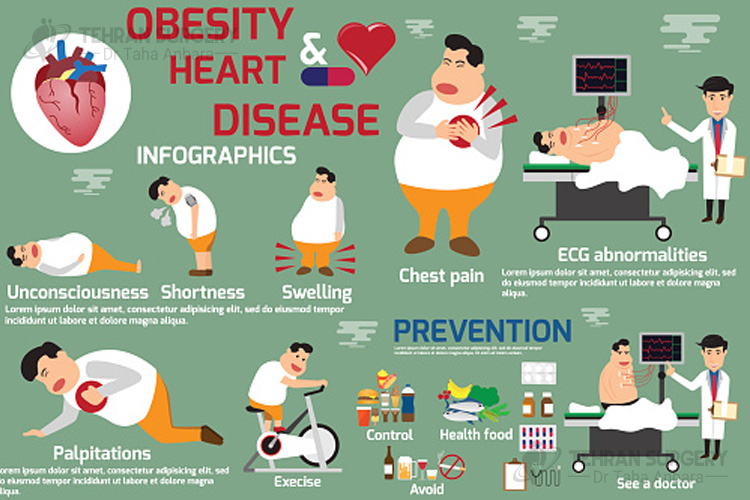
Obesity is a health condition that can cause many serious diseases such as high cholesterol, type 2 diabetes, fatty liver, heart disease and some type of cancers. Because of the rise in the prevalence of obesity, the number of people who suffer from fatty liver disease is increasing, too.
What is fatty liver?
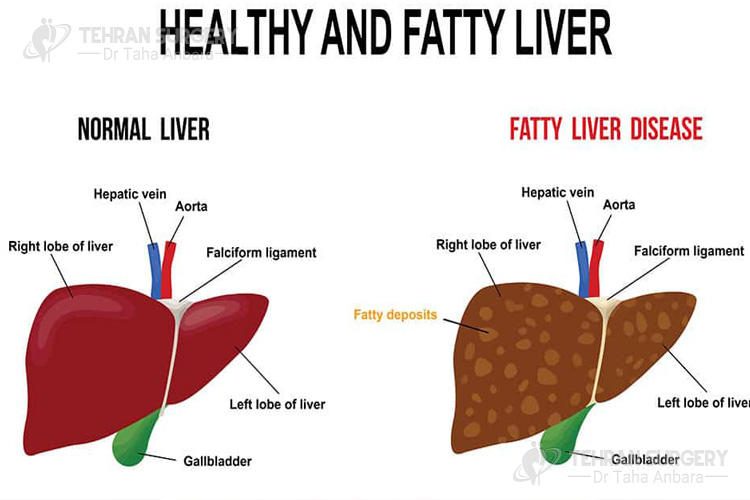
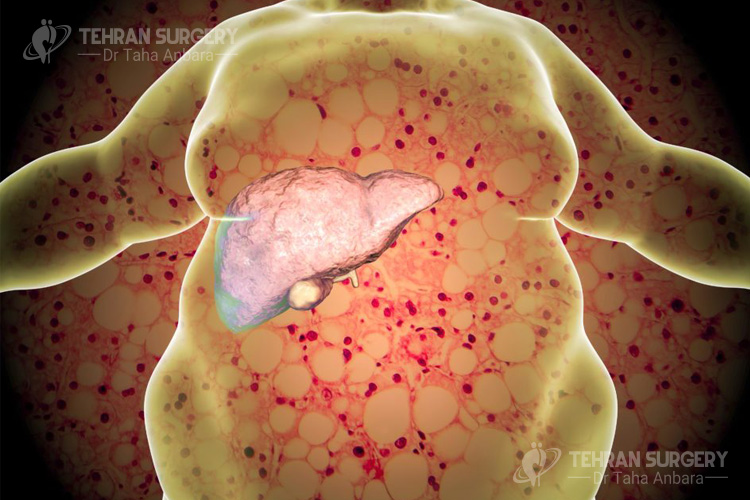
Fatty liver also called hepatic steatosis occurred due to building up fat in the liver. There are two types of fatty liver, alcoholic fatty liver, and nonalcoholic fatty liver.
When the cause of building fat around the liver is not due to drinking too much alcohol it called nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). It is the most common liver disease and around 90 percent of obese patients suffer from fatty liver.
There are also two kinds of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
- Simple fatty liver. In this type, although you have fat in your liver there is little or even no inflammation or liver cell damage.
- Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. This kind of fatty liver is associated with inflammation and liver cell damage as well as fat in the liver.
Symptoms of fatty liver disease
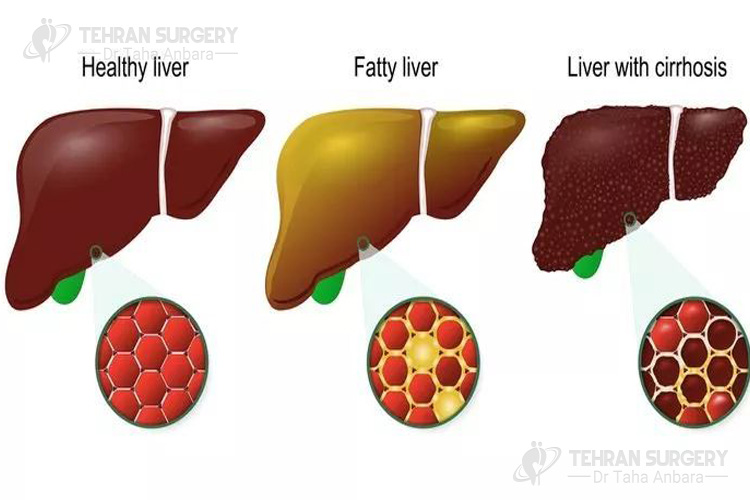
There are some complications associated with fatty liver such as liver scarring which also known as liver fibrosis. Severe liver fibrosis is known as cirrhosis that may cause some symptoms including:
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Abdominal swelling
- Itchy skin
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling of legs
- Weight loss
- Confusion
- Web-like clusters of blood vessels under the skin
- Yellow skin and eyes
Fatty liver causes
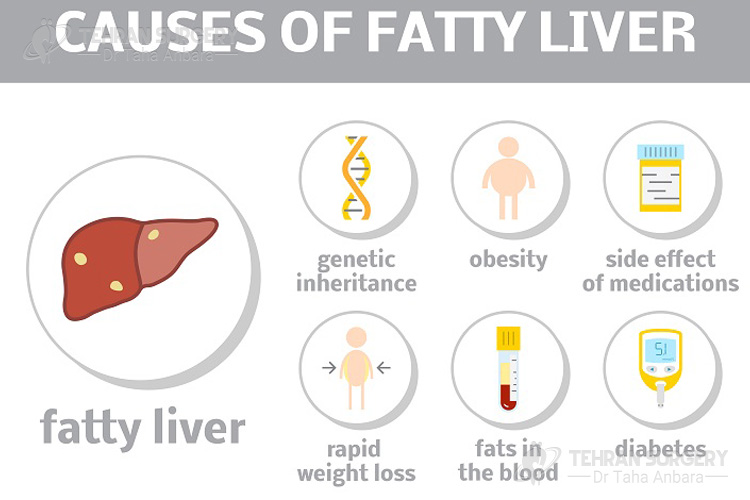
When the body builds up too much fat or doesn’t metabolize fat efficiency it causes fatty liver. Drinking too much alcohol causes alcoholic fatty liver but the causes of nonalcoholic fatty liver are less clear. But there are some factors that are contributed to the fatty liver including:
- Obesity
- Insulin resistance
- High blood sugar
- High level of fat, especially triglycerides in the blood
There are also some less common causes such as:
- Rapid weight loss
- Pregnancy
- Exposure to certain toxins
- Side effects of taking some medications such as tamoxifen, methotrexate, amiodarone, and valproic acid
- Some types of infection such as hepatitis C
- Certain genes also increase the risk of fatty liver
Fatty liver treatment
The first step to treat fatty liver is lifestyle changes. Usually, doctors advise to:
- Take steps to lose weight
- Limit or avoid alcohol
- Change your diet
- Medications
- Surgery
It is also recommended patients with the fatty liver follow a healthy diet including low calories, saturated fat and trans fats as well as to do exercise at least 30 minutes per day.
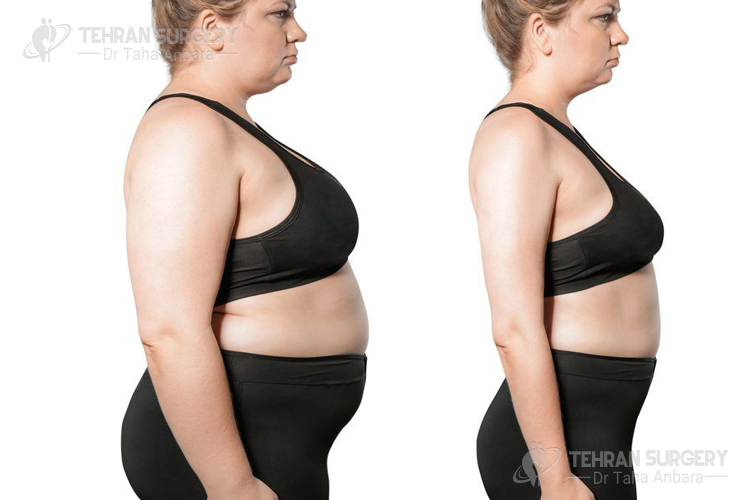
Bariatric surgery is another treatment option for obesity which is associated with fatty liver disease. Weight loss surgery is a way to lose weight for obese people who couldn’t lose weight by different diet plan and exercise. There are different types of bariatric surgery but the most common types are sleeve gastrectomy surgery and bypass surgery.
Relationship between obesity and fatty liver disease
When people start to gain weight due to low activity level, genetic differences, lifestyle habits, and other factors, their pancreas can’t produce enough insulin in order to control the level of blood sugar and blood fat (cholesterol). The liver helps to process and adjust the amount of sugar and fat in the blood but if this process starts to break down and the liver store excess fat in its own cells, the nonalcoholic fatty liver will occur. In case of building up too much fat or presence of a certain genetic condition, fatty liver may be inflamed and liver cells damage or destroy. If this condition continues, it will lead to cirrhosis, permanent scarring of the liver, that can destroy the liver’s ability to function.