Obesity and type 2 diabetes

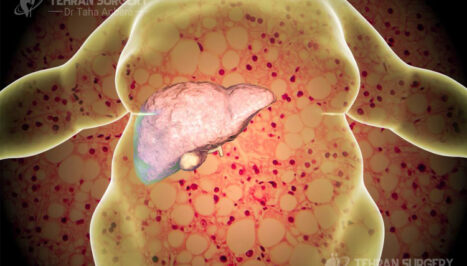
Overweight or obesity is a medical condition that defines as excessive or abnormal fat accumulation. People with a BMI of 30 or more are considered obese and people with a BMI of 25 or more are overweight.
Obesity can affect the overall health and cause some chronic disease such as type 2 diabetes, cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
Obesity causes and risks
Generally, the main reason for obesity is an imbalance between calorie intake and consumption. When you consume more calories than what your body needs, you gain weight. Other factors such as age, gender, genes, family lifestyle, socioeconomic, environmental factors and even your emotions as well as eating disorders can associate with obesity.
Obesity can also increase the risk of many diseases and health problems such as diabetes (type 2 diabetes), heart disease, stroke, lung disease, sleep apnea, high blood pressure, depression, and dementia.
What is type 2 diabetes

Type 2 diabetes is a chronic medical condition and the most common form of diabetes. This disease prevents the body from using insulin the right way and also affect the way body metabolizes sugar. Usually, adults affected by type 2 diabetes but today children are also being diagnosed with this disease and the main reason is because of childhood obesity. More addition many people diagnosed as prediabetes; it means although their blood glucose is not normal it is not high enough to be diabetes.
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes
The symptom of type 2 diabetes is mild and many people don’t realize the symptoms in the early stages.
- Frequent urination and increased thirst. Because of creating excess glucose in the bloodstream, the body will extract fluid from tissue. Consequently, it causes excessive thirst and the need to drink and urinate more.
- Increased hunger. The cells of peoples with type 2 diabetes can’t access glucose for energy so the muscles and organs will be low on energy and they feel hungrier than usual.
- Blurred vision. High blood glucose cause fluid to be pulled from the lenses of the eyes and lead to swelling and temporarily blurred vision.
- Infection and sores. Since blood circulation is poor by type 2 diabetes as well as other nutritional deficits, infections, and sores take longer time to be recover.
- Fatigue. Lack of glucose in cells causes the body becomes tired.
- Gradually putting on weight. Being overweight increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.
There are also some other symptoms such as headaches, leg cramps, itching, skin infections and sometimes weight loss.
Diet for type 2 diabetes
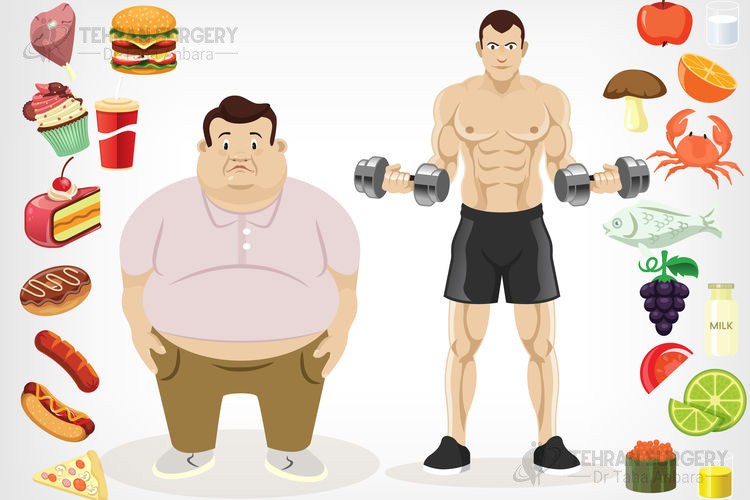
Your diet is effective on the health of your heart and blood glucose levels within a safe and healthy range. People with type 2 diabetes should follow the healthy diet same as everyone including:
- Eat meals and snacks on time
- Choose foods that are high in nutrients but low in empty calories
- Don’t overeat
- Consider food labels before usage
They also should avoid some foods and beverages or limit their usage such as:
- Sugary drinks such as fruit juices
- Pasta or white rice
- Baked goods like bagels and white bread
- Organ meat including liver or beef
- Processed snacks
- High-fat dairy products
- Shellfish
- Processed meats
Peoples with type 2 diabetes can eat healthy carbohydrates, heart-healthy omega-3 fatty acids and monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats such as:
- Sweet potatoes
- Non-starchy vegetables
- Legumes like beans
- Tuna
- Salmon
- Flax seeds
- Halibut
- Oils such as peanut oil, olive oil, and canola oil
- Avocados
- Nuts like pecans, almonds, and walnuts
Causes and risk factors
Generally, when the body becomes resistant to insulin or when the pancreas is unable to produce enough insulin, type 2 diabetes will occur. Although its reason is not clear, some factors such as genetics and environmental factors like being overweight and inactive are associated with type 2 diabetes.
There are also some factors that increase the risk of type 2 diabetes such as fat distribution, family history, age, race, gestational diabetes, prediabetes, and polycystic ovarian syndrome.
Type 2 diabetes treatment
Treatment of this disease needs to lifestyle changes and medication. You should modify your blood sugar levels with diet and exercise. Losing extra weight can help to treat type 2 diabetes, for example, a person who weighs 180 pounds, he/ she should lose about 13 pounds to change his/her blood sugar. Propels with type 2 diabetes should follow a healthy diet and regular exercise for at least 30 to 60 minutes of physical activity per day such as swimming or walking.
Bariatric surgery or weight loss surgery is also another treatment for type 2 diabetes. Many obese people who undertaken gastric sleeve surgery have shown no signs of diabetes after the operation.