Bariatric surgery risks and complications

Weight loss surgery also called bariatric surgery is minimally invasive techniques causes weight loss by limiting the amount of food that stomach can hold as well as reducing the medical health problems associated with obesity. But same as any other surgical procedure, weight loss surgery is associated with some related risks and complications such as infection, bleeding, dumping syndrome, anesthesia problems, weight gain or failure to lose weight and inability to eat a certain food. But risks and complications of bariatric surgery are very less than obesity complications.
Bariatric surgery is the best solution for obese people with body mass index (BMI) 30 or above who need more than diet and exercise. People with BMI 30 to 35 are categorized in class 1 obesity, BMI of 35 to 40 are class 2 obesity and class 3 obesity is BMI 40 or more. Class 2 and 3 obesities, which also called severe obesity, are difficult to manage by diet and exercise alone. In this condition weight loss surgery is the right and effective solution.
The most common weight loss surgeries are bariatric surgery, sleeve surgery, adjustable gastric band surgery and biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch. Some of them affect how the food will be digested and how nutrients will be absorbed. So complications and side effects following the weight loss surgery are vary depending on the type of procedure. According to the JAMA analysis, the rate risk of gastric band surgery is 0.86%, for sleeve gastrectomy 2.2% and 3.6% for gastric bypass operation.
All these weight loss surgeries have common risks and complications as well as some specific risks that are related to each type of bariatric surgery as bellow.
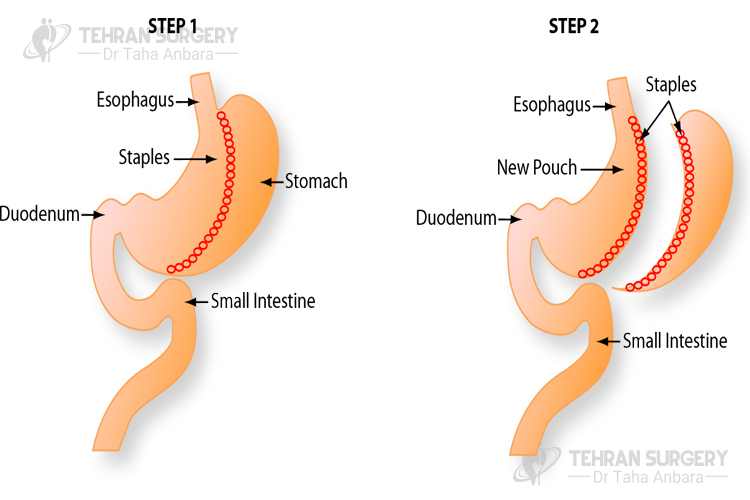
Gastric bypass risks and complications
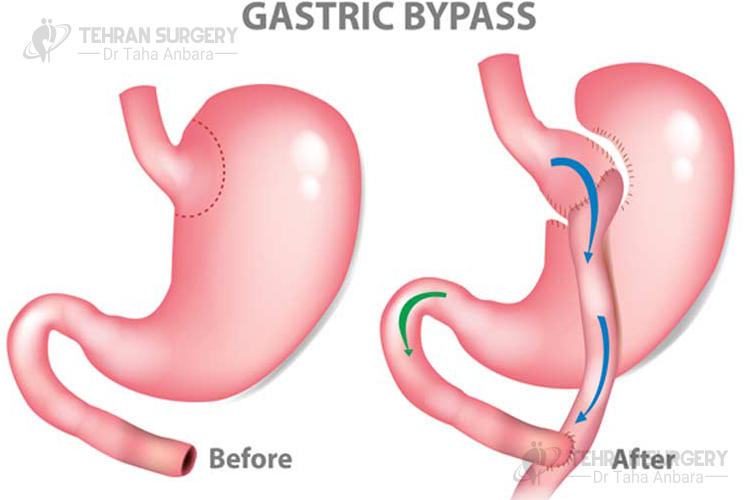
Despite all benefits of gastric bypass surgery, it is associated with some related risks and complications following the surgery including:
- Since bypass surgery limits the quantity of food you can eat as well as the kind of food so it affects the nutrients that your body is able to absorb. You need to see a nutritionist to avoid malnutrition from vitamin deficiency following the gastric bypass surgery. It is recommended to take vitamin supplements such as vitamin B12, Vitamin B1, calcium, and iron.
- Dumping syndrome. Following the gastric bypass surgery, some patients may experience dumping syndrome. It means dumping a solid part of a meal directly from the stomach into the small intestine without being digested. Dumping syndrome may occur in two types, early dumping (occurs 15-20 minutes after eating) that its symptoms include nausea, dizziness or fainting, bloating and abdominal cramps, heart palpitations, rapid heartbeat, and sweating. Late dumping (occurs one to three hours after eating) that comes with symptoms such as confusion, hunger, sweating and heart palpitations, fatigue, tremors, and fainting.
- Stomal stenosis. It occurs when the new opening between the stomach and intestine get tighten and narrow after the bypass surgery.
- It may develop due to stomach leak. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the smooth membrane that lines the cavity of the abdomen. Its symptoms are back pain, fever, restlessness, hiccups, increasing abdominal pain, unexplained tachycardia (rapid heart rate) and pelvic pressure.
Sleeve gastrectomy risks and complications
Although related complications with sleeve surgery are rare, it is associated with some risk like any other surgery including:
- Leaks at the staple line. This may happen in about 1% of patients who underwent sleeve gastrectomy. In this condition, repeated surgery may be required or in case of a persistent leak, it may lead to a fistula forming or recurring infection within the abdomen.
- Inability to tolerate food intake. Some patients who have done sleeve gastrectomy may can’t tolerate sufficient food intake that can lead to malnutrition.
Adjustable gastric band risks and complications
This type of weight loss surgery is associated with some complications such as:
- Band slippage or prolapse. It occurs when the band migrates from its right position which causes prolapse of the stomach above or below the band.
- Port or tubing malfunctions. This complication includes leakage of saline that may causes inflate the band, tubing malfunction or fracture, port rotation or migration.
- Pouch dilation. Band operation and overeating can lead to pouch dilation. It is a pouch enlargement due to higher pouch pressures.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). It is common among patients who undergone banding surgery and present like reflux in other patients.
- Band erosion. It is a serious complication that may lead to weight gain, dysphasia, sepsis, abdominal pain, and hematemesis.
Risks and complications of biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch
- Vitamin and mineral deficiency. People who have undergone BPD/DS may develop kidney stones, osteoporosis, and anemia. More addition they are at high risk for iron deficiencies and calcium as well as thiamine deficiency.
- Protein-energy malnutrition. In severe condition, it is also known as Kwashiorkor that causes by malnutrition.
Despite all the risks and complications of bariatric surgery, it is still the best solution for obese people. If you consider obesity complications such as life-threatening disease including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, stroke and also some cancers, you will find that the bariatric surgery risks are much less than obesity complications.