What is laparoscopic surgery?
Laparoscopy is a type of surgery that a thin instrument and camera insert to the small incisions inside the abdomen or women pelvis. This surgery is applied to find out problems such as cyst, adhesions, infection, fibroid and even for obesity surgery.
A tissue sample can be taken from any part of the body for biopsy by laparoscope.
more information: Excessive Obesity Treatment by Laparoscopic Surgery
Are you a good candidate for weight-loss surgery?
In many cases, laparoscopic can be used rather than laparotomy. A laparotomy surgery involving larger incisions through the abdomen. In contrast, laparoscopy containing less stress, difficulties and expense for minor surgeries. This is an outpatient surgery and no need to overnight hospital stay.
When it’s done?
Laparoscopy instruments and techniques are used for different surgeries such as knee and shoulder surgery. The laparoscopy procedure, which is applied in many different surgeries, is as bellow:
- Removal of diseased organs such as the gallbladder or appendix
- Removal or repair of diseases part of the colon or stomach (digestive system)
- Removal or repair of the bladder, ureters, or kidneys (Urinary system)
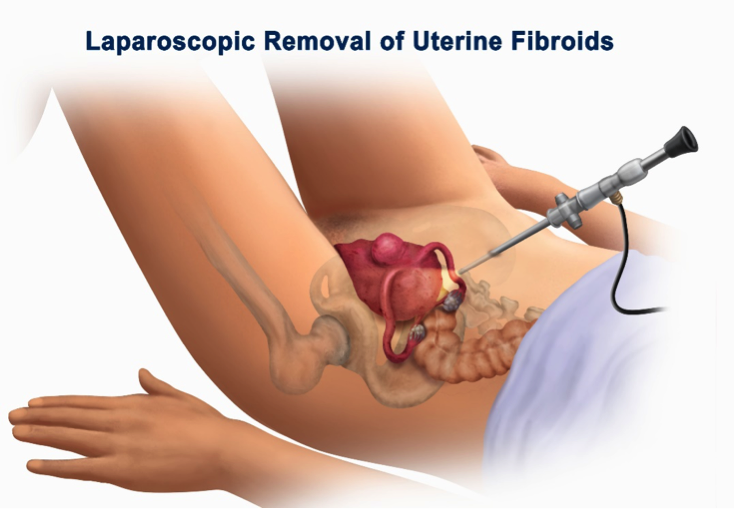
- Removal or repair of women’s reproductive organs, such as the uterus or fallopian tubes
- Tubal ligation
- Removal of a kidney in a living donor
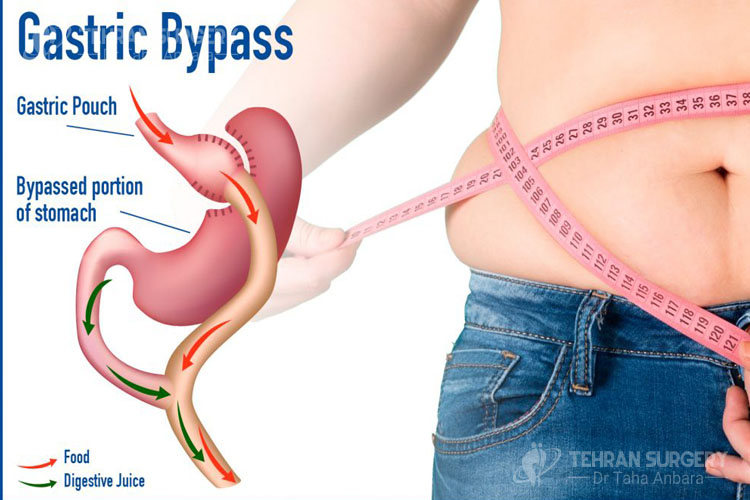
- Weight-reduction procedures, such as gastric bypass
- Repair of a hernia
- To view the liver and pancreas for the presence of cancer tumors
- To view the liver and pancreas for the presence of cancer tumors
- To view the abdomen for signs of disease that has been difficult to diagnose (exploratory surgery)
- To view a tumor in the abdomen
- To check the source of abdominal pain or remove scar tissue
- To look for the source of internal bleeding or fluid buildup if the patient has a normal blood pressure
- To view injury following trauma or an accident
Laparoscopic preparation

If you have allergic reaction to a drug during anesthesia or have bleeding problems and use of any kind of blood thinners like aspirin or warfarin (Coumadin) or if you are pregnant, you should inform your doctor.
How it’s done?
Laparoscopic surgery is outpatient surgery and no need to overnight stay in hospital. This surgery can apply in hospital or clinic. Usually, general anesthesia provides in this surgery. The patient is sleep during the procedure and don’t feel any pain.
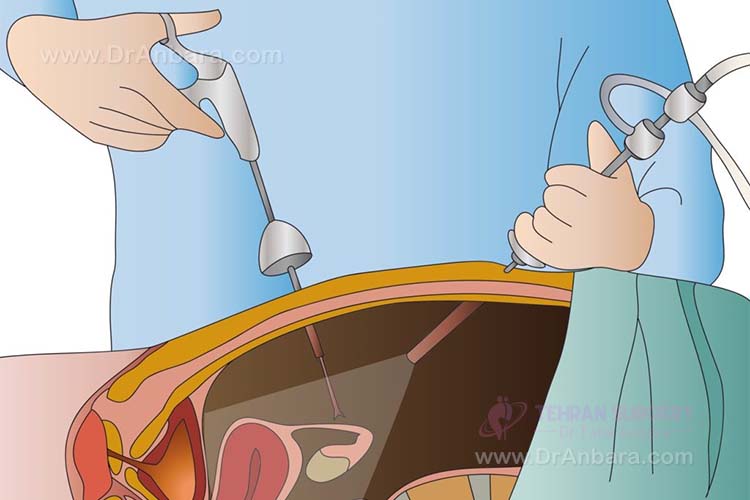
In some cases, surgery can be performed under local anesthesia and the intended part will be cut while you are awake and can’t feel any pain. During laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes some cuts that are 6-12 inches. Then a thin tube called canola insert the body to fill the stomach with carbon dioxide gas to expand it in order to provide surgeon more room to view the organs.
When abdomen is extended, the surgeon inserts the laparoscope into the abdomen. The camera attached to the laparoscope display the inside organs on a screen and surgeon can see live inside the abdomen.
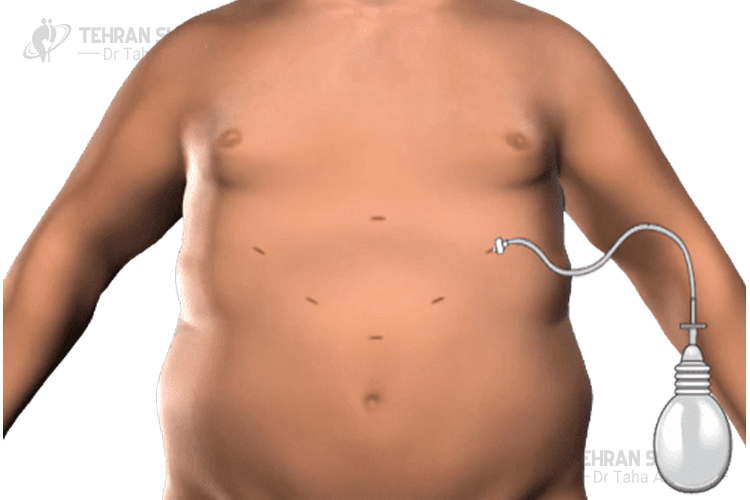
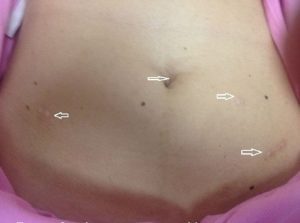
The number and size of the incisions are depending to the special disease that surgeon try to distinguish or prevent it. Generally, there is 2-5 cuts in this surgery that surgical instruments are inserted to the body through these incisions.
When all stages are accomplished, the abdomen will relieve of dioxide gas and instruments will exit of the abdomen. Finally, cuts are blocked with stitch or bandage.
Result of laparoscopic surgery
The surgery results depend on medical finding and applied method. Usually, patient recover with minimal pain and difficulty because they have just small incisions to heal.
If you face with any following problems, inform your doctor as soon as possible:
- Headache or fever
- Vomiting or nausea
- Bleeding, redness or drainage from any of the small incisions
- Swelling of the surgical area
- Inability to urinate
- Pain that can’t be heal by prescribed medication
After laparoscopy
- Some pain and difficulty is possible for the small cut were made. In this condition, your doctor may prescribe pain reliever.
- If stitches were used, they will remove after one or two weeks according to your doctor diagnosis.
- Sometimes carbon dioxide gas can cause pain in shoulders. The same nerves that reach to the shoulder are exist in the diaphragm and may irritate diaphragm. This pain goes away during the times.
- The gas pressure that cause emergency and repeated needs to urinate goes away over the times.
- Your doctor will determine when eating and drinking can be resumed.
- When a patient is recovered sufficiently, he/she can come back home but he can’t drive immediately after release.
The next steps after laparoscopy
If laparoscopy surgery is done to diagnosis a disease or to view the diseased organ, the patient needs to see the surgeon to go over the surgery results. If it is done for another targets, should follow the surgeon advices. As long as you are not fully recovered, you should avoid strong activity and heavy lifting.
Laparoscopy risks
Laparoscopy surgery rarely follow by complications, but as any other surgery, infection is a side effect. There is possibility of bleeding in the abdomen and scars may develop. Anesthesia during surgery may cause heart attack, stroke and pneumonia but these consequences rarely occurred.
During the laparoscopy surgery, there is the possibility of the following risk:
- The surgeon may puncture a blood vessel or an organ unintentionally. This fault can lead to bleeding or damage to the organ.
- The scar tissue from previous operation can make difficulty to proper insert of trocars (a surgical instrument with a cutting point, used to access blood vessel and provide access port during surgery) into the stomach. Scar tissue can prevent the gas extension into the abdomen.
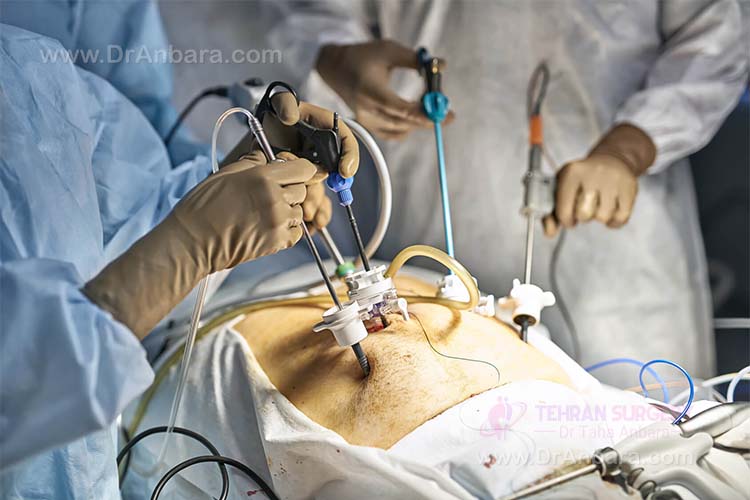
If complications develop or are found, the surgeon may decide to make a larger incision and follow the standard surgery procedure rather than laparoscopy. However, the surgeon certainly considers the patient health as a priority before decision making.
If the surgery complications develop, there is tow option for surgeon:
- Anti-biotic prescribe for infection control
- Blood transfusion in order to replace lost blood
Laparoscopy surgery is more complex for who are obese. Most doctors suggest people to lose weight before surgery. Although, nowadays there is special loss weight surgery such as laparoscopy.
How safe is laparoscopy surgery?
Laparoscopic surgery is as safe as traditional open surgery. At the beginning of laparoscopic surgery, the laparoscope insert through a small incision close to the belly button. The surgeon first considers the stomach organ in order to check whether laparoscopic is danger for patient or not. If body organs are inflamed more than standard or surgeon encounters other factors that prevent a clear view of the structure, the surgeon may make a larger incision for a safe and secure operation.
Any intestinal surgery may associate with certain dangers such as anesthesia complications, bleeding or infection. An individual general health and other medical conditions are effective factors for surgery risks. You should consult with your doctor your individual risk for any operation.